
People might say that ‘life begins at 40.’ But with age also comes a whole host of physical problems you’ve never felt when you were younger.
Sometimes, Body pain is inevitable. That’s why you must know what the general aches most older adults experience to get preventive treatment as soon as possible.
9 Types Of Body Pain: Causes & Treatments
Here’s a list of the common types of body pain and how to treat them:
1. Hip And Pelvic Pain

What is body pain? As you get older, your calcium levels decrease. The lack of calcium in your body causes various issues, including the deterioration of the bone. Hip fractures are common causes of hip pain due to the brittleness of bones that comes with old age. The fractures may get worse after a fall. Body Pain can also happen due to a variety of reasons like:
Tendinitis
The inflammation or irritation of the tendons around hip bones can cause hip Body Pain. The pain may worsen after the overuse of these tendons.
Bursitis
Bones, tendons, and muscles have liquid sacs between their tissues called bursae. These sacs reduce the friction when the tissues rub together. Pain happens when the bursae become inflamed. Overuse and repetitive stress on the hip joints inflame the bursae.
Avascular Necrosis Or Osteonecrosis
When blood flow to the hip slows down, the bone tissue dies. Osteonecrosis can happen to other bones, but this often happens to hip bones. Hip dislocation or fractures are some of the causes of osteonecrosis.
You’ll know you have hip pain when you feel discomfort in your buttocks, groin, inside or outside of the hip joint, and thighs.
2. Arthritis And Joint Pain

Almost 50% of people over the age of 65 experience arthritis, but better health choices early in life can help you avoid this.
Arthritics has many types, but the two most common types are:
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Body Pain- This pain happens over time through the overuse of your joints. Repetitive movement after an injury can also cause OA. When you have OA, the cushions on the ends of your bones wear out until your bones end up rubbing against each other.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
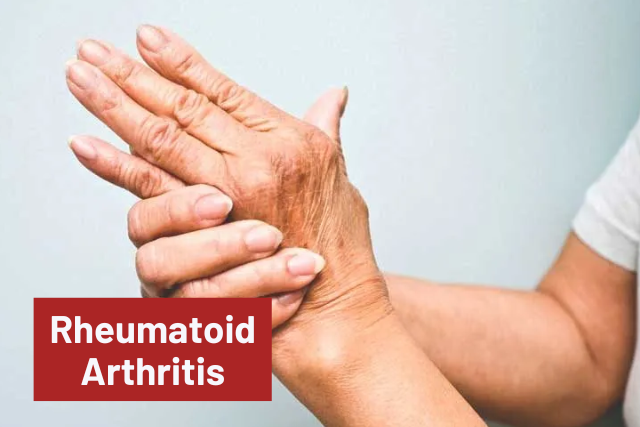
Body Pain- This pain is an inflammatory condition. Your immune system attacks tissues that line your joints. You may feel tenderness, warmth, or stiffness on swollen joints, as well as fatigue, fever, and lack of appetite.
To prevent the early signs of arthritis, you could eat a balanced diet with anti-inflammatory food like nuts and oily fish and regularly practice low-impact exercises like yoga and walking. NSAIDs and topical pain relievers may also relieve the pain.
3. Lower Back Pain
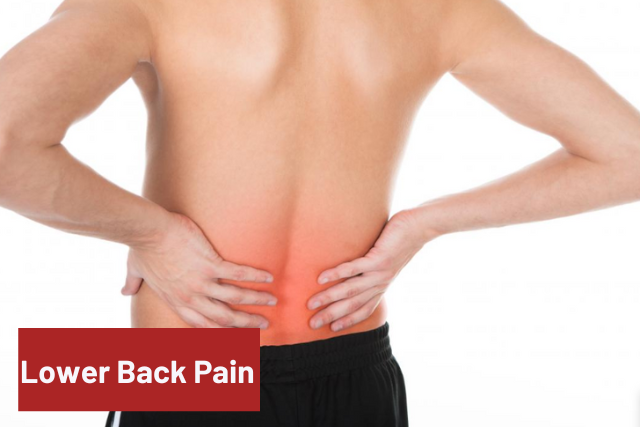
Body Pain- People over 60 are more likely to experience spinal and back pain than their younger counterparts. Lower back pain can limit your daily movement and even sleep.
Some symptoms that may manifest due to back pain are:
- Back stiffness in the morning and evening;
- Leg pain when standing or walking; and
- Limited flexibility and height loss.
You’ll feel sensitivity or tenderness on the affected area. Walking long distances may also trigger pain. Sitting or lying down reduces the pain almost immediately. Intermittent back pain body could develop into chronic pain if you regularly suffer from stress or depression.
If you’re suffering from back pain, you can check these top four ways to relieve it or try these other methods:
- Take medications like NSAIDs;
- Try acupuncture;
- Undergo physical therapy; and
- Get help from a chiropractor.
Body Pain- As with any ache, you might be tempted to rest as often as you can. Try not to stay in bed too much, though. Physical activity releases chemicals that block pain signals and strengthen muscles. Always choose exercises that are appropriate for your age.
4. Headaches

Body Pain- Headaches affect many people in their 20s to their 50s, but they may worsen the older they get. Migraines, cluster headaches, and tension often cause headaches for older adults. Medication overuse is also a possible cause.
A headache can also impair daily activities. Assess the symptoms you’re feeling alongside the headaches and talk to your doctor.
To treat a headache, get enough sleep. Rest prevents headaches from getting worse. You may also do these other lifestyle changes:
- Try yoga and meditation exercises;
- Eat a balanced diet; and
- Avoid triggers (bright lights, loud noises, caffeine).
Other than these methods, you may want to consider alternative treatments to control the pain and cope better.
5. Carpal Tunnel

Body Pain- People in their mid-40s to mid-60s are more prone to suffering from carpal tunnel. The nerve that runs from your arm to your palm is either squeezed or pressed.
This condition causes pain, numbness, or tingling in your wrist and fingers and is results from repetitive movements like writing or typing.
If you have this condition, your doctor may recommend you to do carpal tunnel exercises or take over-the-counter (OTC) medication. For severe cases, doctors will suggest surgery.
6. Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia is the medical word for muscle wasting. The older you get, the more at risk your muscles get weak, too. Muscles get weakened because they no longer absorb and use nutrients the same way they did when you were younger.

Older adults sometimes also have smaller appetites, hence the lower likelihood of eating more healthy food. You lose muscle mass when these factors combine.
When your muscles lose vitality, simple activities may become painful. A sneeze may make you overstretch and end up swelling your muscles in pain. Weakened muscles on your legs and feet may cause a loss of balance.
How to treat body pain for relief. Primary treatments for older adults with sarcopenia are a healthy diet and exercise —physical activity such as strength or resistance training.
Weights can help increase muscle strength, while resistance bands increase endurance. Always get the advice and assistance of a professional physical trainer before undergoing such exercises.
7. Muscle Pains And Strains
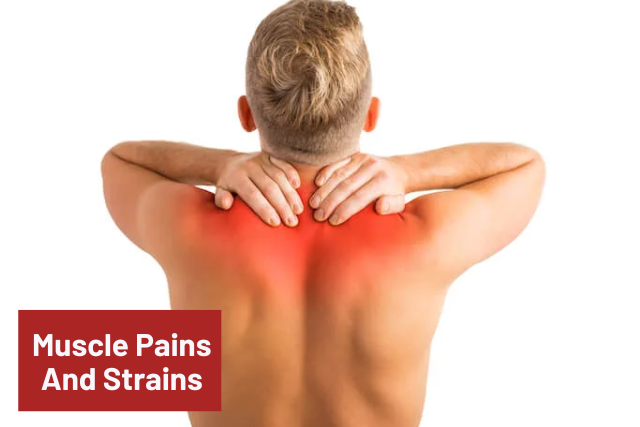
As you age, so does the structure of your muscles. Fibers become less dense and more prone to injury due to inflexibility. If you enjoy doing low-intensity physical activities like chores or gardening now, you may have to be careful with yourself as the year’s pass.
Avoid getting yourself hurt as much as possible. Injuries from the past may come haunting you in the future. If you feel the first signs of muscle pain or strain, it’s time to pay a visit to your doctor.
They may suggest you take OTC medicines for body pain or do RICE therapy, which is short for:
- Rest the injured part for around 48 hours
- Ice the affected area 20 minutes, at least 4 to 8 times a day
- Compress to reduce possible or further swelling
- Elevate the injured area 6 to 10 inches above the heart
Exercises like Pilates or yoga that focus on stretching the muscles may help in preventing future aches. So, while you’re still able to move around a lot, try it out to keep your muscles strong and supple.
8. Fibromyalgia
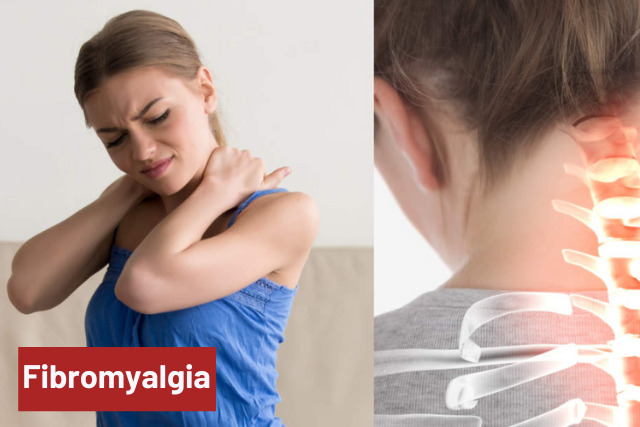
While still in the same vein of muscle aches, fibromyalgia is a type of chronic pain in which you’ll feel pain all over your body. Unfortunately, medical researchers and professionals still don’t know what causes this.
, they believe it’s a neural condition in that it affects how your brain receives and processes pain signals. You might be feeling intense pain in your body when in reality, it’s nothing more than a needle prick.
Fibromyalgia may be caused by physical trauma, a stressor, or may manifest gradually out of nowhere. Some symptoms you should watch out for are:
- Cognitive issues or poor memory;
- Fatigue;
- Mood swings;
- Muscle pain; and
- Sleep problems.
You may be prescribed medication like anti-seizures, anti-depressants, and muscle relaxers to deal with this chronic pain. Acupuncture and massage therapy may also relieve fibromyalgia.
9. Bone Spurs
Calcified growths on the neck, shoulders, spine, hands, knees, hips, and heels cause this ache in many older adults. By itself, the spur isn’t painful. In some cases, pain in the lower back, neck, and joints manifests because these growths press nerves, tendons, or ligaments.
You may not even know you already have a bone spur unless you get your x-ray taken. Or, you’ll only know you have it when you start feeling pain in other parts of your body. When your doctor confirms that you have bone spurs, common treatments to relieve pain and swelling include:
- OTC like Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, and Naproxen sodium;
- Bed rest;
- Physical therapy; and
- Steroid shots.
Your doctor may change your medication if your intake of the OTC given to you lasts more than a month. When the other above treatments don’t work either or worsen pain symptoms, you may need body surgery to remove the bone spurs.
If you already have other pain, such as arthritis, the risk of you getting bone spurs is also high. However, you can prevent bone spurs from manifesting due to other factors by:
- Increasing calcium and vitamin D in your diet;
- Wearing shoes with good arch support and a wide toe box and wearing thick socks; and
- Losing weight.
Early arthritis treatment is one good way to avoid future bone and joint damage that starts the growth of these bone spurs.
Pain Prevention:
Due to various internal and external factors, getting body aches as you get older seems to go hand in hand. But that isn’t to say they’re entirely unpreventable.
With regular checkups, exercise, and a healthy diet, you can prevent body pain from happening or lessen the symptoms. Continue or begin a healthy lifestyle as early as possible to ensure a longer, fruitful life.
