Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral illness typically affecting young children. It is caused by any one of several viruses belonging to the Enterovirus family, including coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses (such as the virus responsible for poliomyelitis).
HFMD is usually mild and often goes away within a week or two. Symptoms can include fever, fatigue, mouth sores, loss of appetite, and a rash with blisters on hands, feet, legs, and sometimes the buttocks.
In rare cases, it can lead to more severe complications like encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) or meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain).
Parents must be aware of symptoms and contact their child’s doctor if necessary. Also, practicing good hygiene habits, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent the spread of this virus.
It is important to note that although HFMD is typically seen in young children below 5 years old, it can affect people of any age.
Anyone who experiences these symptoms should seek medical attention as soon as possible to help lessen the severity and duration of the illness.
Without treatment, HFMD can lead to more serious, potentially life-threatening complications.
What Is Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosed & Treatments
Causes
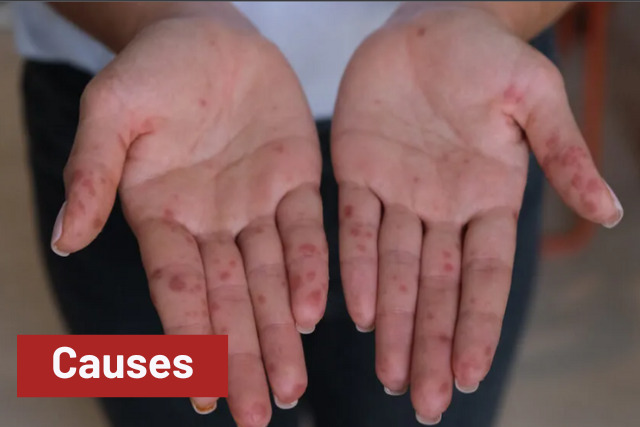
It is caused by any one of several viruses belonging to the Enterovirus family, including coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses (such as the virus responsible for poliomyelitis).
Symptoms
It can include fever, fatigue, mouth sores, loss of appetite, and a red rashes, like Psoriasis on hands, feet, legs, and sometimes the buttocks.
Mode Of Transmission
The virus that causes HFMD is spread from person to person through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or stool (poop). This can occur when an uninfected person touches surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touches their mouth, nose, and/or eyes.
How Is Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease Diagnosed?
HFMD can be diagnosed based on medical history and physical exam. Blood tests or throat swabs may also be ordered to confirm a diagnosis.
What Are The Complications Of Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease?
In rare cases, HFMD can lead to more severe complications like encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) or meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain).
Without treatment, HFMD can lead to more serious, potentially life-threatening complications. It also involves:
- Dehydration: Losing fluids through vomiting and/or diarrhea can lead to dehydration.
- Respiratory complications: Rarely, HFMD may cause breathing issues due to the virus entering the lungs.
- Glomerulonephritis: This type of kidney inflammation rarely occurs but can be severe if it does.
- Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle that can result from HFMD infection. It is usually mild but can become severe in some cases.
- Nail loss: In some cases, the virus can cause permanent nail loss.
Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease Prevention
- Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and running water is the best way to reduce the spread of HFMD.
- If a child shows any signs or symptoms, they should be taken to a doctor immediately for diagnosis and treatment.
- Parents should remind children about proper hygiene practices, such as not sharing food, toys, or utensils with other children who may be infected with the HFMD virus.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces in the home regularly to help stop the spread of the virus from one person to another.
- Avoid close contact with people who have symptoms of HFMD, such as fever, coughing, sneezing, and sore throat, until their condition improves.
- If you or your child has HFMD, it is essential to take steps to prevent the virus from spreading to other people. This includes not attending school or daycare until the symptoms have resolved.
- It is also essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands often, covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue (or elbow), and disposing of tissues appropriately.
Treatment
How to treat Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease?
- Rest and plenty of fluids are essential for managing HFMD.
- Over-the-counter medications may be used to help reduce fever and relieve pain.
- In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication such as acyclovir which can help reduce the severity of signs and shorten the duration of the Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease illness.
- Anesthetic ointments or creams can also be applied to mouth sores to relieve discomfort.
- For severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous fluids and monitoring of other vital signs.
- In rare cases, surgery may be required if the virus has caused deformities in the hands or feet that need to be corrected.
- A doctor may also recommend a vitamin supplement to help boost immunity and reduce the risk of infection.
- More aggressive treatments may be necessary if complications arise, such as encephalitis or meningitis.
FAQs
How Do You Catch Your Hand, Foot And Mouth?
HFMD is spread from person to person through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or stool (poop). This can occur when an uninfected person touches surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touches their mouth, nose, and/or eyes.
What Are The Long-Term Effects Of HFMD?
The long-term effects of HFMD depend on how severe it is and what complications occur during the illness. In mild cases, there usually are no long-term effects. However, in more severe cases, the virus may cause permanent damage to the brain or other organs.
How Does A Kid Get Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease?
The virus that causes HFMD is spread from person to person through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or stool (poop). This can occur when an uninfected person touches surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touches their mouth, nose, and/or eyes.
Can You Get Hand, Foot And Mouth Fisease More Than Once?
Yes, a person can get HFMD more than once, as immunity does not constantly develop after having the illness. However, people who have had HFMD may be less likely to catch it again since they will likely have some level of protection against reinfection.
Can Adults Get Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease?
Adults can get HFMD, although it is more common in children under 10. Adults who become infected may experience milder symptoms than children since their immune system is likely exposed to the virus.
However, adults should take precautions to prevent spreading the virus to other people. Both adults and children with HFMD must practice good hygiene, such as washing hands often and covering coughs or sneezes with a tissue (or elbow).
Conclusion:
HFMD is an infectious disease caused by viruses from the Enterovirus family, such as coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses (poliomyelitis virus).
