
Thyroid eye disease name is also called Thyroid Orbitopathy is an eye problem that affects the soft tissues of the eye that border or is adjacent to the eyes. the foremost noticeable symptoms include inflammation and swelling of the tissues triggered by an abnormal immune response.
As the swelling continues, so does the space within the eye and as a result, the eyeball is hard-pressed. The cornea in effect isn’t adequately protected by the eyelid. The movement of the attention ball within the eye is restricted because of the reduced functionality of the muscles in the eye. Here are Thyroid eye disease Symptoms, causes & Treatments.
What is Thyroid Eye Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis, stages & Treatments
Thyroid eye disease, or TED, is characterized by protrusion of the eyeball. It is most prevalent in Graves’ disease, which is caused by an overproduction of hormones or hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid.
Thyroid disease affects the eyea , which become inflamed and push the eyeball forward. Other causes may include eye infections, dilated blood vessels, and tumors. Swelling can occur in one or both eyes.
Eighty percent of all TED patients suffer from Graves’ disease due to hyperactive thyroid. Other cases include Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Hashitoxicosis, or atrophic thyroiditis.
Signs & Symptoms Of Thyroid Eye Disease
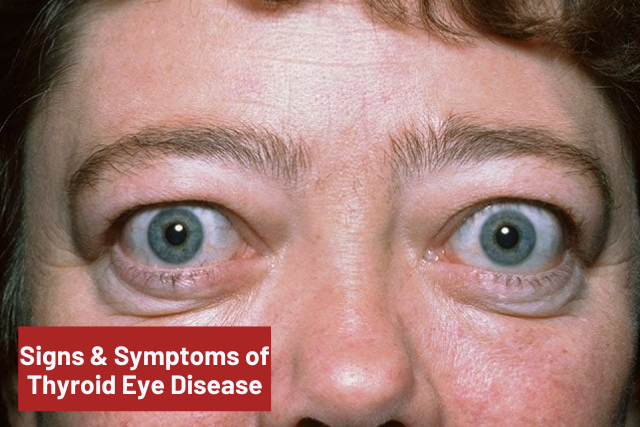
- Proptosis (exophthalmos or bulging),
- Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye)
- Dryness
- Eyelid retraction
- Eyelid lag
- Twitching
- Redness
- Itching
- Double vision
- Retrobulbar pain
- Pain on or behind the eye
- Chemosis (edema or swelling)
- Swelling
- Blurriness
- Eye muscle paralysis
- Corneal irritation leading to corneal inflammation
- Difficulty moving the eyes
- Foreign body sensation
- Formation of scar tissue
- Lacrimation (tearing)
- Sensitivity to light
- Upper eyelid droop
- Staring
- Visual impairment
Diagnosis

Thyroid eye disease can only be diagnosed by examining the eyes of people who have already been diagnosed with thyroid gland problems. The diagnosis takes the following form:
Blood Test

This happens when the doctor thinks the initial diagnosis needs to be backed up. Hormones in the blood are measured to find out how your thyroid gland works. A blood test is called a thyroid function test. A more complex test can also be performed to measure antibodies.
Scan
Sometimes the doctor will need to do a scan to assess how active the thyroid gland is. If orbital inflammation is alarming, a scan called a magnetic resonance image scan is performed. This is a more comprehensive scan that reveals more affected tissue.
Other Tests
Your ability to distinguish between colors and your vision to determine how good your peripheral vision is is thoroughly examined. Eye movement is also checked to find out how much damage is being done to the muscles.
Treatment For Thyroid Eye Disease:
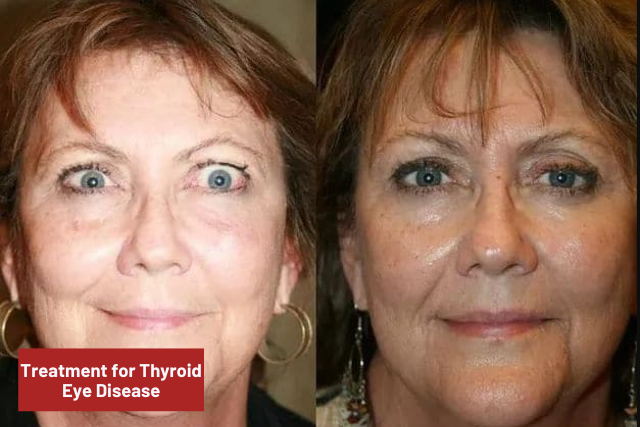
Thyroid eye disease is a condition that is caused by an overactive thyroid gland. In other words, it is when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, causing it to produce excess thyroid hormone. This extra thyroid hormone affects the eye muscles causing them to become enlarged and stiff. And that’s why you may see your eyes bulge out, feel dryness in your eyes, and even notice vision problems. so that’s why you know about how to treat Thyroid Eye Disease.
1. Orbital Decompression Surgery
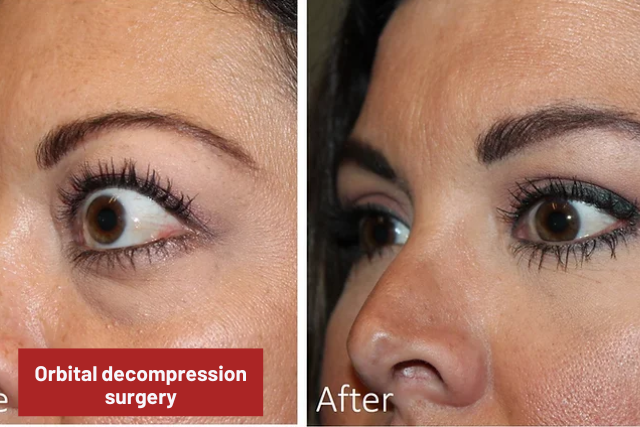
Involves removing the bone between the orbit (the cavity holding the eyeball) and therefore the surrounding sinuses. this enables more room for swollen tissues behind the eye leading to decreased eyeball protrusion and reduction of nervus opticus pressure.
2. Eye Muscle Surgery
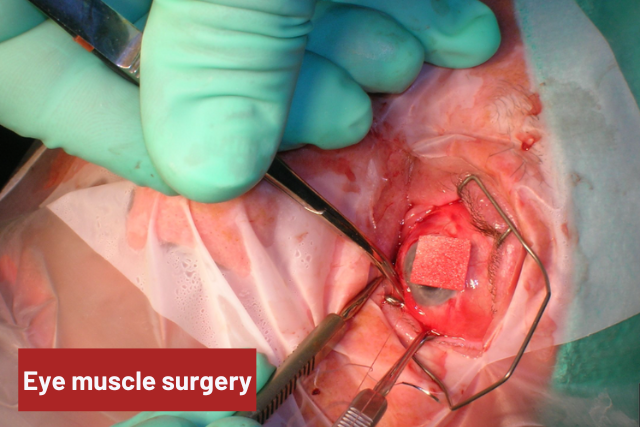
This procedure aims to correct the misaligned eye muscles, improving single vision in the straight-ahead gaze and therefore the downgaze. However, proper eye alignment may require over one surgery.
3. Eyelid Surgery
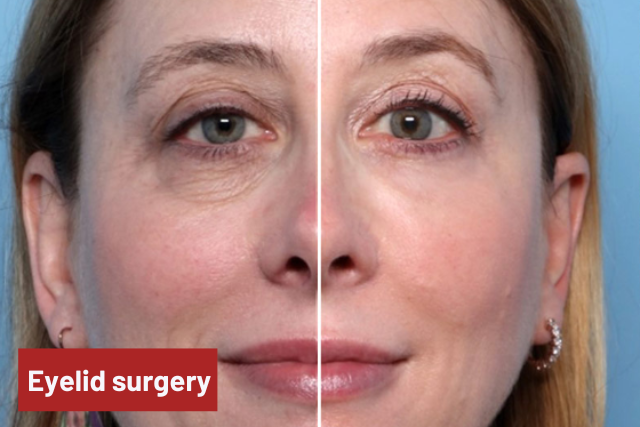
In Graves’ ophthalmopathy the eyelids open more widely. The surgery on eyelids is performed to correct this to provide a glance that’s as near to normal as possible.
Eyelid surgery will be useful to lower the upper eyelids and to boost the lower eyelids. This surgery is also outpatient surgery. Both upper and lower eyelids will be operated simultaneously, and fat will be far from the upper and lower eyelids to scale back the incidence of swelling of the upper and lower eyelids.
Surgery is combined with a sculpture of the upper or lower lids, to get rid of swollen fat and excess skin, to put the eyelid in a less wide-open position and lessen the surprised look, and to line the eyelid crease in a natural position.
Also Read
- lifetime-fitness-membership-prices-locations
- membership-levels-at-lifetime-fitness
- What is Ursolic acid? Benefits, Side effects and Supplements
- 5 Best Ingredients to Increase Testosterone Levels Naturally
- 6 Benefits of Biotin – How It May Protect Your Health
- Keto Diet Advantages And Disadvantages
- Planning Meals: 4 Factors To Consider – Complete Guide
- How-much-is-a-day-pass-at-lifetime-fitness
- What-does-a-virtual-medical-receptionist-do
